What is Engine? An engine is a Device or a machine that is designed to convert one or more energy forms into mechanical energy or motion energy.
HEAT ENGINES AND THEIR TYPES
The engine or machine that converts heat energy from the combustion of fuel or any other source and converts this into mechanical work is called a HEAT engine.Heat engines can be broadly classified into two main categories.
A. External combustion engines (E.C. engines)
B. Internal combustion engines (I.C. engines)
A. External combustion engines (E.C. Engines)
The engines in which the combustion of fuel takes place outside the cylinder are known as external combustion engines. In these types of engines, the heat of the combustion of fuel is transferred to the second fluid (water is converted into steam) which is the working fluid of a cylinder e.g., steam engines or a steam turbine plant.IN steam engines, the heat of combustion is employed to generate steam which is used in piston engines or turbines. These engines are mainly used for driving locomotives, generation of electric power, etc.
B. Internal combustion engines (I.C. Engines)
The engines in which the combustion of fuel takes place inside the cylinder are known as internal combustion engines. Petrol, gas, and diesel engines are the examples of internal combustion engines. In these engines, the products of combustion are directly the motive fluid.
FOUR-STROKE PETROL ENGINES OR SPARK IGNITION (S.I.) ENGINES
It’s also known as an auto-cycle engine. The for-stroke petrol engine takes a change in the form of an air-fuel mixture.(Petrol mixed with a proportional quantity of air in the carburetor). The cycle of operation is as follows:
Let’s Understand How this engine works
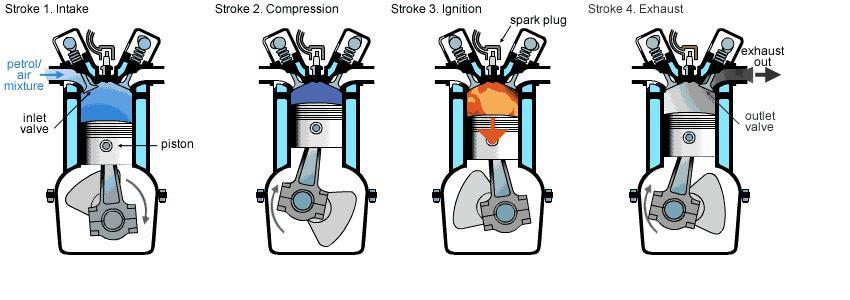
- 1. Suction stroke
- 2. compression stroke
- 3. Power stroke
- 4. Exhaust stroke
1. Suction stroke
During this stroke, the inlet valve is opened and the outlet valve is closed. When the piston moves down from the TDC (TOP DEAD CENTER), a partial vacuum is developed inside the cylinder. As a result, the mixture of air and petrol is closed into the cylinder. When the piston reaches the BDC (Bottom dead center), the inlet valve closes. The flywheel makes a half-revolution.
2. compression stroke
During the compression stroke both the inlet and outlet valve remain closed. The piston rises from the BDC to TDC and the flywheel makes another half-revolution. The mixture, which was sucked into the cylinder during the suction stroke, is compressed in the combustion chamber. The heat produced during the compression vaporizes the mixture. When the piston reaches the TDC, a spark is produced in the spark plug. This spark ignites the spark plug.
3. Power stroke
Both the inlet valve and exhaust valve remain closed during the power stroke. The burning gas expands and pushes the piston down to the BDC. When it reaches the BDC, the exhaust valve opens. The flywheel turns by another half-revolution.
4. Exhaust stroke
During the exhaust stroke, the inlet valve is closed and the exhaust valve is open. The piston rises up from the BDC to the TDC. When the burnt gas is pushed out of the cylinder, the exhaust valve closes and the inlet valve opens with the flywheel making another fresh mixture of air and petrol drawn into the cylinder. The cycle of suction, compression, power, and exhaust strokes is then repeated. Thus for every cycle of operation, the flywheel rotates twice.
These are all the processes you need to do to start the engine, that will work well for your car. we use petrol engines and diesel engines to run a car.
FAQs
What enery source are used to run a car engine?
What is cc in engine?
How much cc is 1 hp?
What is engine braking?
What is engine protect in car insurance?
I hope this information will be helpful for you and if you want me to write an article on other topics you can comment down below and I will write about it. I’m not a good writer but I will try my best to provide you well-researched Article that will be informative for you.
Thank you
You May like to Read










